Fulgorid planthoppers
The family Fulgoridae is a large group of hemipteran insects, especially abundant and diverse in the tropics, containing over 125 genera worldwide. They are mostly of moderate to large size, many with a superficial resemblance to Lepidoptera due to their brilliant and varied coloration. Various genera and species (especially the genera Fulgora and Pyrops) are sometimes referred to as lanternflies or lanthorn flies, but neither do their heads emit light, norare they even distantly related to flies.
The head of some species is produced into a hollow process, resembling a snout, which is sometimes inflated and nearly as large as the body of the insect, sometimes elongated, narrow and apically upturned. It was believed, mainly on the authority of Maria Sibylla Merian, that this process, the so-called lantern, was luminous at night in the living insect. Carl Linnaeus adopted the statement without question and coined a number of specific names, such as laternaria, phosphorea and candelaria to illustrate the supposed fact, and thus propagated the myth.
จักจั่นงวง เป็นแมลงที่มีสีสันโดดเด่นชนิดหนึ่ง ปีกมีลักษณะเป็นเยื่อบางบาง หลายชนิดมีงวงยื่นออกมาจากส่วนหัวคล้ายงวงแต่บางชนิดไม่มีลักษณะดังกล่าวเลย ลักษณะเด่นของแมลงในวงศ์ Fulgoridae คือ ปีกมีลักษณะเป็นเยื่อ มีลวดลาย สีสัน และเส้นขวางปีกจำนวนมาก มีฐานหนวดขนาดเล็กอยู่ใต้ตา ปกติมีส่วนยื่นออกมาจากส่วนหัว การจำแนก ใช้ สีสันและลวดลายของส่วนปีกเป็นสำคัญ จักจั่นงวง มีขาแบบเดิน (walking lake) ขาคู่หลังมีลักษณะพิเศษที่ช่วยให้เอาตัวรอดจากการคุกคามของศัตรู มันสามารถดีดตัวออกจากที่มันเกาะอยู่ เมื่อถูกรบกวน แต่หากถูกจับส่วนใหญ่จะแกล้งตาย เมื่อศัตรูเผลอจะดีดตัวและบินหนี ขณะบินสีสันที่โดดเด่นทำให้มองเห็นคล้ายผีเสื้อ
จักจั่นงวงขณะเกาะ จะหุบปีกแนบกับลำตัว ปากมีลักษณะเป็นแบบเจาะดูด กินน้ำเลี้ยงของพืชเป็นอาหาร จักจั่นงวงมีขนาดตั้งแต่ 2 – 8 เซนติเมตร เมื่อถึงวัยเจริญพันธุ์จักจั่นงวง ตัวผู้จะมีขนาดเล็กกว่าตัวเมีย การผสมพันธุ์และการวางไข่ ส่วนใหญ่จะพบบริเวณพืชอาหาร หลังฟักจากไข่ ตัวอ่อนจะทิ้งตัวร่วงลงสู่พื้นดิน และขุดลงไปอาศัยอยู่ใต้ดิน เพื่อดูดกินน้ำเลี้ยงจากรากพืชเป็นอาหาร ทั่วโลกพบแล้วกว่า 670 ชนิด เอเชียและออสเตรเลียพบแล้วกว่า 236 ชนิด ในประเทศไทย พบจักจั่นงวง 7สกุล 30 ชนิด จากการสำรวจธรรมชาติ ยังพบว่าจักจั่นงวงมีความสัมพันธ์กับสิ่งมีชีวิตชนิดอื่น เช่น แมลงสาบ หรือแม้แต่จิ้งจก ซึ่งจะมากินของเสียที่จักจั่นงวงขับถ่ายออกมา
เทคนิคการถ่ายภาพจักจั่นงวง ควรจับจักจั่นงวงเวลากลางคืน เมื่อมันแกล้งตาย ให้กางปีกออก และค่อยๆปล่อยให้มันเกาะกับต้นไม้ จึงถ่ายภาพ หากไม่มั่นใจควรจับจักจั่นงวงไว้ในมือแล้วจึงถ่ายภาพเพื่อใช้อ้างอิงในการจำแนกโดยภาพถ่าย หลายคนให้ความสนใจจักจั่นงวง ถือเป็นสัตว์นำโชคขณะเดินป่า ปัจจุบันมี ผู้สนใจธรรมชาติเพิ่มขึ้นมากมาย ศูนย์วิจัยกีฏวิทยาป่าไม้ที่ 1 จึงได้รวบรวมรูปจักจั่นงวงที่พบในประเทศไทย เพื่อให้ผู้ที่สนใจได้เปรียบเทียบชนิดต่อไป
Suborder: Auchenorrhyncha
Superfamily: Fulgoroidea
Family: Fulgoridae
ในประเทศไทย พบ 3 Subfamily คือ Subfamily Aphaeninae ,Subfamily Fulgorinae และ Subfamily Hemiptera
| Subfamily Aphaeninae | Tribe: Aphaenini
| Aphaena aurantia var. apicata (Distant), 1906 Aphaena submaculata burmanica (Didtant), 1906 Aphaena najas ( Schmidt), 1906 Kalidasa nigromaculata (Gray), 1832 Polydictya uniformis (Walker), 1857 Polydictya tricolor ( Westwood ), 1845 Penthicodes ( Ereosma) bimaculata (Schmidt), 1905 Penthicodes ( Ereosma) variegate (Guerin-Meneville), 1829 Penthicodes ( Ereosma) atomaria ( Weber), 1801 Penthicodes ( Ereosma) pulchella (Guerin-Meneville),1838 Penthicodes ( Ereosma) caja (Walker), 1851 |
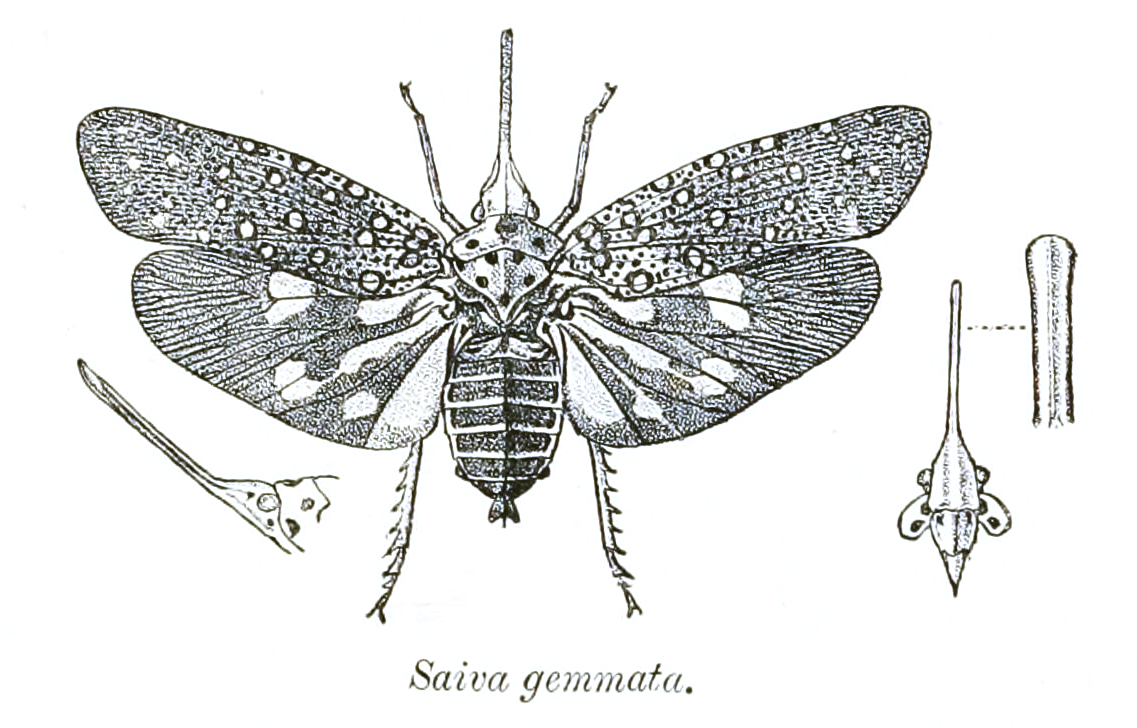
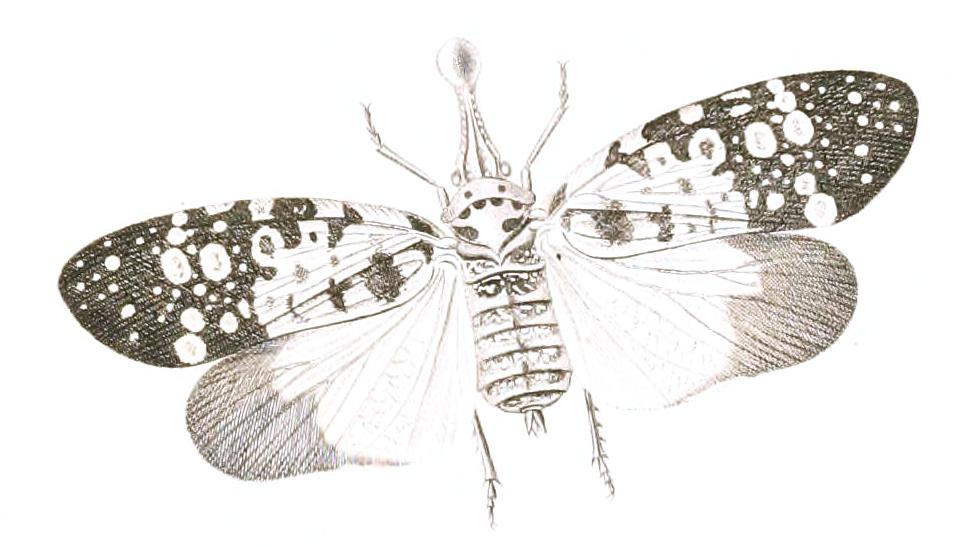
| Subfamily Fulgorinae | Tribe: Laternarini | Pyrops spinolae (Westwood), 1842 (Fulgora nigrirostris (Walker), 1858)Pyrops viridirostris (Westwood),1848 Pyrops candelaria (Linnaeus),1758 Pyrops ducalis ( Stal). 1863. TYPE : Londres Pyrops astarte ( Distant ), 1914 Pyrops clavata mizunumai ( Sato & Nagai), 1994 Pyrops peguensis ( Schmidt), 1911 Pyrops lathburii ( Kirby ), 1818 Pyrops oculata ( Westwood ), 1839 Pyrops shiinaorum shiinaorum (Nagai & Porion), 2002 Saiva gemmata (Westwood), 1848 Saiva cardinalis (Butler),1874 Saiva bullata ( Distant),1891 |
Tribe: Zannini
| Zanna terminalis ( Gerstaecker), 1895 Zanna dohrni ( Stal), 1858 Zanna nobilis ( Westwood ) , 1839 Zanna chinensis ( Distsnt ), 1893, TYPE : Londres |
( ที่มา https://www.dnp.go.th/FOREMIC/NForemic/this_month/fulgorid/fulgorid%20bug.htm )
Subfamily
Aphaeninae
🔴Aphaena submaculata burmanica (Didtant), 1906

🔴Aphaena najas ( Schmidt), 1906
 |
| ดอยหัวหมด กย.25 |
🔴Penthicodes ( Ereosma) atomaria ( Weber), 1801
จักจั่นงวงกุดใต้ปีกแดงใหญ่
Penthicodes atomaria can reach a length of about 55 millimetres (2.2 in), with a wingspan of about 50 millimetres (2.0 in). The pronotum is yellow, the head and the scutellum are brown, while the abdomen is reddish with a few small white spots. The upper side of the forewings is whitish at the base and brown at the marginal, with four black spots. The upper side of the hindwings is red, with many black spots and two large black marking at the apex.
 |
| กาญจนบุรี |
Penthicodes pulchellus is a species of planthoppers in the subfamily Aphaeninae(Fulgoridae): found in southern India, Indo-China and Malesia. It belongs to the subgenus Ereosoma Kirkaldy, 1906.[3][4] The genus name was formerly treated as feminine, but in 2022 it was revised to masculine in accordance with ICZN Article 30.1.4.4,[note 1] changing the spelling of this species' name from pulchella to pulchellus.
Penthicodes variegatus is a species of planthoppers in the subfamily Aphaeninae(Fulgoridae): found in South-East Asia. It belongs to the subgenus Ereosoma Kirkaldy, 1906. The genus name was formerly treated as feminine, but in 2022 it was revised to masculine in accordance with ICZN Article 30.1.4.4, changing the spelling of this species' name from variegata to variegatus.
The species differs from other species by its tegmina with large dark-brown markings, ground colour of tegmina and membrane brown; white patch along su-tural margin and costal margin on nodal line of cross-veins. The subspecies malayanus is is very easy to rec-ognize from P. caja caja by the disc of hind wings red as opposed to orange in P. caja caja.Material examined. Thailand: 1 ♀, Nakhon Ratchasi-ma Prov., Mu Si, 21.III.2020, W. Khaikaew leg. (LTRS)
Subfamily
Fulgorinae
Fulgoridae, commonly known as lanternflies, are a family of planthoppers found in Thailand. A catalog of Thai specimens held at the Natural History Museum of Thailand lists 33 species in 10 genera. Seven species are newly recorded for Thailand, including Polydicta tricolor, Pyrops ducalis, Pyrops karenius, Pyrops oculatus, Pyrops pyrorhynchus, Saiva bullata, and Saiva cardinalis. ResearchGate notes that three species, Pyrops connectens, Pyrops spinolae, and Zanna nobilis, were first recorded from Khao Krachom Mountain in Thailand.Tribe: Laternarini
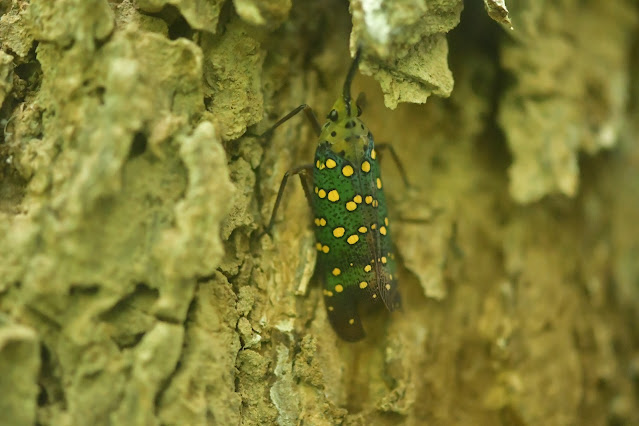
Genus: Saiva ในประเทศไทย พบ 4 ชนิด
🟠Saiva gemmata (Westwood), 1848
Chiang Mai, Thailand, IV.1990
Dwarf Lanternfly
จั๊กจั่นงวงน้อยจุดกลม
Saiva gemmata is the type species of the genus Saiva, which are lantern bugsfound from the North-East of India to Indo-China (Thailand and Vietnam). No subspecies are listed in the Catalogue of Life.
 | |||||
🟠Saiva cardinalis (Hemiptrea, Fulgoridae) Doi Inthanon (Chiang Mai, Thailand) Saiva cardinalis[is a species of lantern bug in the genus Saiva, found to the North-East of India (Darjiling, Sikkim), Nepal and Vietnam. 🟠Saiva constanti Jianaraisakul จั๊กจั่นงวงเรียวภูเขา A new species of the Asian lanternfly genus SaivaDistant, 1906 from Thailand (Hemiptera: Fulgoromorpha: Fulgoridae) with notes on S. virescens(Westwood, 1842) and Pyrops cultellatus (Walker, 1857) | เชียงใหม่ มิย 25 |
Genus: Pyrops ( Lantern fly )
ในประเทศไทย พบ 10 ชนิด
🔵Pyrops karenia (Distant) 1891
จั๊กจั่นงวงกะเหรี่ยง
Pyrops karenius, also known as the Red-nosed Lanternfly, is a species of planthopper belonging to a group commonly referred to as lantern-flies. This species is found in Burma, Thailand and the Karen Hills of India. The head, its protrusion and the thorax are reddish brown. The cephalic process is slightly recurved and its tip is flattened.
 |
| เชียงใหม่ |
🔵Pyrops ducalis ( Stal). 1863.
TYPE : Londres Cambodge
Pyrops ducalis is a species from the Fulgoridae family of lanternflies. The head, thorax and abdomen are orange to red, with the head brightened apically. The forewings (tegmina) are green with green spots, with the basal half and area at two-thirds of the tegmina white. The basal patch of the hindwings is white or luteous. The shape of the cephalic process combined with white areas on tegmina will differentiate it from all species but P. coelestinus, from which it differs by having a red, not brown, cephalic process; dark green, not yellow, spots on the tegimen; and a different pattern of white on the tegmina.
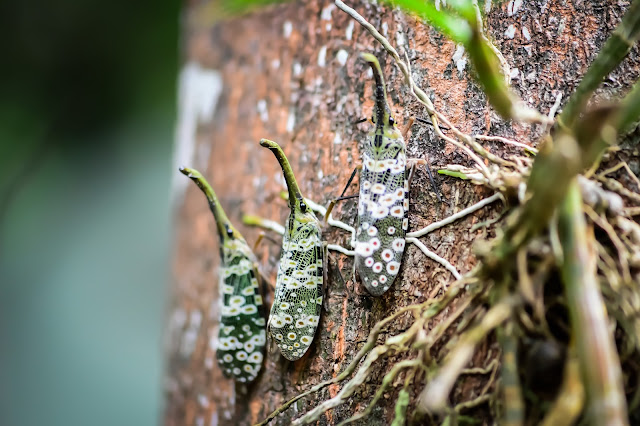
🔵Pyrops spinolae (Westwood), 1842
Cuo- phuong, prov.Ninh Binh. Viet-nam, II.VI.1966,R.Bielawski & R.Pisaraki leg. (Varsovie)
จั๊กจั่นงวงดำ
Pyrops spinolae is a species of planthopper sometimes referred-to as the dark-horned lantern-fly (Vietnamese: ve sầu đầu đen). The species is named after Maximilian Spinola, the authority for the genus. This lantern bug is recorded from Indiaand Indochina. Pyrops condorinusfrom southern Thailand was once considered as a subspecies.
 |
| ปางสีดา |
 | ||
เชียงใหม่
ฟอร์มสีเข้ม |
 |
| Vichai อช.เขาปู่ เขาย่า 04/25 |
🔵Pyrops viridirostris (Westwood)
Chaing Mai, Thailand,VI.1992
จั๊กจั่นงวงเขียว

🔵Pyrops candelaria (Linnaeus),1758
จั๊กจั่นงวงลำใย
Pyrops candelaria (Laternaria candelaria and Fulgora candelaria in older literature) is a species of planthopper[2] often placed in the tribe Laternariini. This species has been recorded from: Guangdong, Guangxi, Cambodia, Vietnam, Hong Kong, Laos, Thailandand other parts of southeast Asia. It is the type of the genus Pyrops erected by Spinola in 1839.
Like all Fulgoridae, P. candelaria feeds on plant sap: including longan and lycheetrees (Sapindaceae), among others. Its long, slender proboscis is used to pierce tree bark to reach the phloem.
Members of this genus are sometimes called lanternflies (although lanternflies do not emit light) because of their notable 'cephalic process'. They are often sought-out by collectors, attracted by their fore wings (see figure), yellow-orange hind wings with a black zone around the wing tips, a reddish head and cephalic process with white spots.
 |
| พบที่เชียงใหม่ |
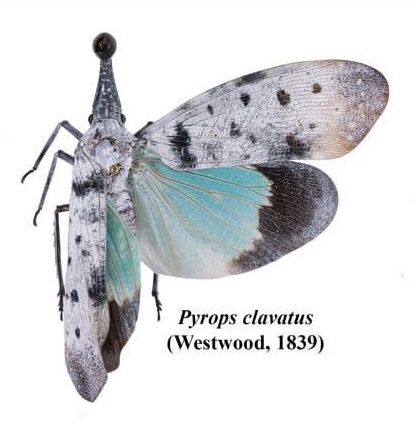
Pyrops clavatus is a species of true bug in the family Fulgoridae, in the genus Pyropswhich are sometimes called "lanternflies". This species is found in parts of northern and northeastern India, Myanmar, northern Thailand, southern China and northern Vietnam.The tip of the elongated head capsule is spheroidal, shiny and chestnut in colour while the remainder of the process is black with fine white spotting. The forewing has a variable patterning of black, grey and white. The hindwing is purplish white with the apical half black. Specimens have been obtained along the Himalayas west to Mussoorie (a specimen of which had the entire cephalic process dull red) but more often in Assam, Sikkim, Shillong and the Khasi Hills.
The species was described by John Obadiah Westwood in 1839 in the Transactions of the Linnean Societyunder the genus Fulgora. The type specimen came from Assam through the collections of Theodore Edward Cantor based on which Westwood described the key features in Latin, noting specifically the upward curve of the cephalic process with its enlarged and rounded dull-brick-red tip, "apiceque adscendente, et in globum subrotundum, subpellucidum, laete testaceum terminato". He also illustrated the specimen in black and white. The middle segment of the upperside of the thorax has a black spot on each side. The underside of the abdomen is reddish.[2] Arthur Gardiner Butler described the tip of the rostrum as bearing a "ludicrous resemblance to a "vesuvian" cigar-light" (a kind of early matchstick used to light cigars).
A paler form which was described as a subspecies mizunumai (Sato & Nagai, 1994) is not considered valid.
🔵Pyrops peguensis ( Schmidt), 1911
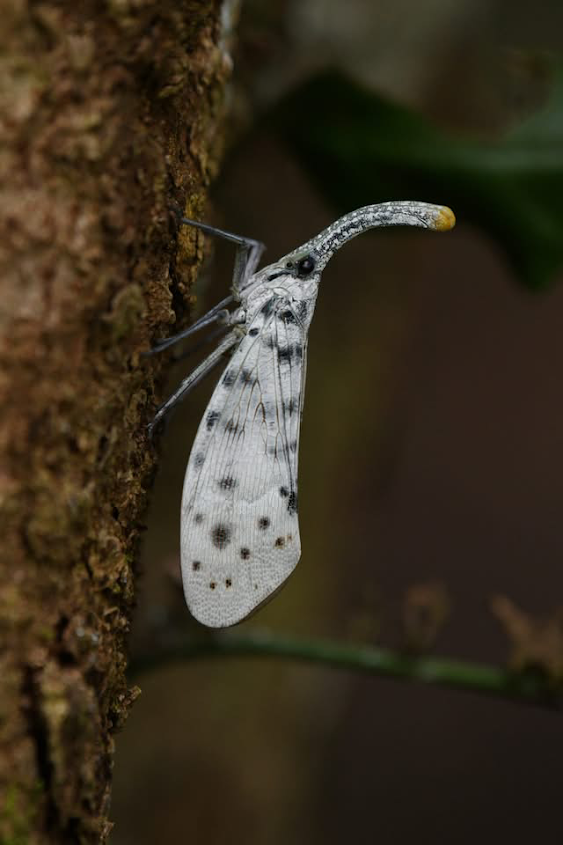
🔵Pyrops lathburii ( Kirby ), 1818
จั๊กจั่นงวงปลายส้มปีกลาย
Pyrops lathburii is a species of lanternfly found in northern India, northern Thailand, southern China, Laos, and Vietnam. Pyrops lathburii is a variable species. Its head, thorax, and abdomen range from brown to black, its hindwings from yellow to white, the apex of its cephalic process from yellow to red, and the tegmen all the way from white with unmargined black spots to black or very dark with yellow, margined spots and green veins. However, it can be identified by the apex of its cephalic process, which is distinctly brightened, but without a similar pattern at two-thirds of the wings as in Pyrops pythicus.
It was previously placed in the pyrorhynchus group; it was moved to the candelariagroup because of its hindwings.
 |
| Somkiat Pakapinyo ดอยอืนทนนท์ มิย 25 |
 |
| น้ำตกสิริภูมิ 16/06/25 |
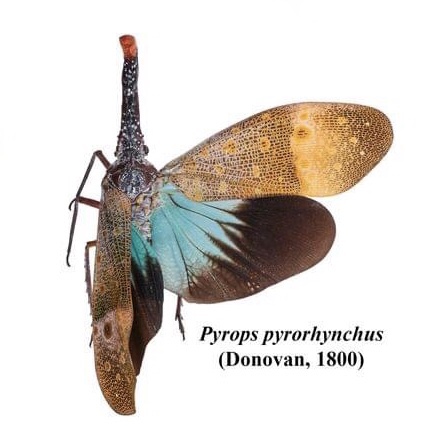
🔵Pyrops pyrorhynchus (Donovan, 1800)
Red-headed Lanternfly
จั๊กจั่นงวงปลายหัวแดง
งวงมีสีแดงปนน้ำตาลถึงน้ำตาลเข้ม ปลายงวงมีสีแดงสด ค่อนข้างกลมยาว
Diagnosis. (1) cephalic process red brown to dark brown, bright red apically; robust and rather straight (2) tegmina green or covered by white waxy with yellow spots, 4 – 5 spots on the white or pale brown band along the nodal line of cross veins (3) posterior wings blue with distal portion black extending along the posterior margin.
Published in: Nagai, S., & Porion, T. (1996). Fulgoridae 2.

 |
| Hala Bala 05/08/25 |
🔵Pyrops astarte (Distant, 1914)
Albino Lanternfly
จั๊กจั่นงวงสีเผือก
There are two color form hindwing with yellow and white.
 Pyrops connectens is a species of planthoppers from the Fulgoridae family. The species is most similar to Pyrops spinolae in colour, but the shape of the cephalic process and the pattern and the size of the spots on the tegmen. The size of the spots on the tegmina will also distinguish it from series with same or similar shape of cephalic process, like Pyrops coelestinus. The base of the hindwing are white or pale blue with 4-5 concolorous spots outside of the patch.
Pyrops connectens is a species of planthoppers from the Fulgoridae family. The species is most similar to Pyrops spinolae in colour, but the shape of the cephalic process and the pattern and the size of the spots on the tegmen. The size of the spots on the tegmina will also distinguish it from series with same or similar shape of cephalic process, like Pyrops coelestinus. The base of the hindwing are white or pale blue with 4-5 concolorous spots outside of the patch.A specimen obtained from Khao Yai since 25.v.18 and kept it too long to work out. Distribution: Recorded from Java ( Guérin-Méneville, 1845) and Sumatra (Nagai & Porion 1996). The wingspan is about 5-5.5 mm.
🔴Kalidasa nigromaculata (Gray, 1832)
จั๊กจั่นงวงเข็ม
Kalidasa is a genus of planthoppers in the tribe Aphaenini of the family Fulgoridae. There are five species in the genus, which are found in different parts of tropical Asia.
Subfamily
Hemiptera
Several subfamilies of the Hemiptera order are found in Thailand, including Auchenorrhyncha (leafhoppers, planthoppers, cicadas, treehoppers, spittlebugs), Sternorrhyncha (scales, aphids, whiteflies, psyllids), and Heteroptera (true bugs). Specifically, within Heteroptera, families like Belostomatidae (giant water bugs), Pleidae, and Miridae (plant bugs) have been studied and documented in Thailand.
A new erythroneurine leafhopper genus from Thailand (Hemiptera, Cicadellidae, Typhlocybinae), with description of three new species
Thailand is home to a diverse array of Heteroptera, with over 230 species representing 12 families found in freshwater habitats. Specifically, studies have documented the presence of species within the Belostomatidae, Aphelocheiridae, Largidae, Pyrrhocoridae, Pleidae, Reduviidae, and Gerridae families. These true bugs are abundant in both still and flowing water systems, including anthropogenic ponds in urban areas.
























































ไม่มีความคิดเห็น:
แสดงความคิดเห็น